by: Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Recently, researcher Tang Yongbing from the Functional Thin Film Materials Research Center, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and his research team used high-voltage and high-concentration electrolyte to significantly improve the energy density and cycle stability of the potassium-based dual-graphite battery. Related research results were published online with the title "6.0 V High-Voltage and Concentrated Electrolyte toward High Energy Density K-Based Dual-Graphite Battery". The famous journal Advanced Energy Materials (DOI:10.1002/aenm.202002567, IF:25.245).
Potassium-based dual-carbon battery (K-DCB) combines the advantages of dual-ion battery with high voltage, low cost, environmental friendliness and abundant potassium resources, and has broad application prospects in the field of large-scale energy storage. As a source of active ions, the electrolyte has a decisive influence on the performance of K-DCB, including capacity, energy density, and cycle life. However, the current electrolyte system based on KPF6 potassium salt and carbonate solvents has a low concentration (<1 m) and insufficient oxidation potential, resulting in poor K-DCB cycle stability and energy density that needs to be improved.
In view of this, researcher Tang Yongbing and his team members Li Xiang, Dr. Ou Xuewu and others have successfully developed a sulfone electrolyte system (KFSI/TMS) with a high concentration of 5.2 m after systematically studying the matching behavior of different solvents and potassium salts. . Compared with the traditional low-concentration electrolyte system, the high-concentration electrolyte shows obvious advantages: First, the high oxidation potential (~6.0 V vs. K/K+) increases the capacity of the anion (FSI-) intercalation graphite cathode And cycle stability; second, the potassium storage performance of the graphite anode is effectively improved; third, the energy density of the potassium-based dual-ion battery has been significantly improved. After 300 cycles of the potassium-based dual graphite battery based on the high-voltage and high-concentration electrolyte system, its capacity has almost no decline. Considering both the electrolyte and electrode materials, the energy density of the K-DCB reaches ~130 Wh kg-1, which is the best performance reported so far. This work confirms the effectiveness of high-voltage concentrated electrolyte for improving battery performance and has guiding significance for the development of high-efficiency and low-cost energy storage devices.
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangdong Science and Technology Plan, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Joint Laboratory, and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Plan.
Paper link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/aenm.202002567
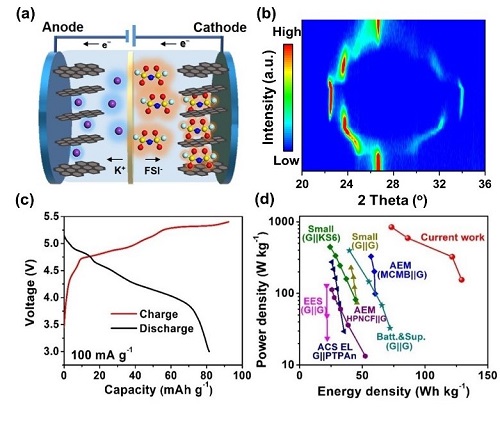
(A) Schematic diagram of the structure and working mechanism of potassium-based dual graphite battery; (b) In-situ XRD characterization of anion (FSI-) intercalated graphite cathode;
(C) Charge and discharge curve of potassium-based dual graphite battery; (d) Comparison with previously reported energy and power density
Source: http://www.siat.ac.cn/kyjz2016/202009/t20200924_5704737.html
Disclaimer: This article is translated by cpolymer. The translation is for reference only. All contents are subject to the original text.