The institute of soil and water conservation (ISWC) has made a series of progress in the research and development of new materials for ecological environment governance
by: Institute of soil and water conservation (ISWC)
In the past five years, She Diao and Zheng Jiyong, associate researchers of the Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have participated in the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772390, 41571225, 31700521), the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0501702, 2017YFC0504504), and the Science and Technology Service Network Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences ( KFJ-STS-QYZD-177) and the Western Young Scholars Project (XAB2018A05) have done a lot of exploratory research around the interdisciplinary research and development of new materials for ecological environment governance, and achieved a series of innovations in the field of new materials for the prevention and control of water and soil environmental pollution As a result, a series of high-performance carbon-based adsorbents, biodegradable composite membranes and other new materials for ecological environment management, with soil conservation, water conservation, fertilizer conservation, and water and soil pollution prevention as the core, have been developed, which has promoted soil science, soil and water conservation, and ecology The cross-integration with materials chemistry and other disciplines has made beneficial exploration for the research and practice of green and high-quality development of ecological environment in China. The research results are mainly published in international journals such as Chemical Engineering Journal and Journal of Hazardous Materials.
1. Developed high-performance carbon-based adsorbent
The high specific surface area "honeycomb" high-performance carbon-based adsorbent developed by adding surfactants combined with pore-forming technology has a Cr(VI) adsorption capacity of 332.53 mg/g, and the initial adsorption after 7 adsorption-desorption 90% adsorption capacity; after process improvement, the adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) is increased to 402.9 mg/g, the adsorption performance is significantly better than similar materials
Using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and other analytical methods, combined with isothermal adsorption and kinetic adsorption models, the adsorption mechanism of phosphate adsorbed by the adsorbent and the adsorption of complexes were revealed This form provides new ideas and techniques for the prevention and treatment of phosphate pollution in sewage and soil and for solving the problems of adsorbent recovery and regeneration.
The above adsorbent preparation process is simple, low cost, excellent performance, green and environmental protection. It provides a green and efficient new idea and method for industrial preparation of carbon-based adsorbents with high adsorption capacity and high reproducibility. It is an energy and mining area in the Loess Plateau. The prevention and control of water and soil environment pollution and land reclamation and ecological restoration provide new theoretical and technical support, and the application prospect is very broad.
Relevant achievements were published in Chemical Engineering Journal, Journal of Hazardous Materials and Environmental Science and Ecology Science of The Total Environment.
2. Developed a biodegradable composite film
Using agricultural and forestry product waste as raw materials, biodegradable composite films with good tensile strength, elongation at break, thermal stability and barrier properties are prepared, which can be used as alternative products for agricultural white mulch. The research result is biomass conversion The use and development of green and environmentally friendly membrane materials provide new ideas and technologies, which are of great significance for the prevention and control of white pollution.
The research results were published in the materials science journal Composites Science and Technology, engineering technology journal Carbohydrate Polymers and engineering technology journal Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers.
3. Developed a lignin-based water-retaining agent
A new biomass-based water-retaining agent, lignin-based hydrogel, was synthesized by using liquid phase cross-linking polymerization method using lignin as a raw material in the paper industry. Compared with the traditionally used acrylamide, this new water-retaining agent has the advantages of being green, degradable, water-retaining and fertilizer-retaining, and the water retained is mostly effective water.
This material can significantly increase the effective soil water content of the soil between 0.3MPa-1.5MPa, and increase the soil's ability to maintain nutrients. Under extreme drought conditions, the water-retaining agent can extend the crop growth time by 10-14 days, provide new materials for dry land agricultural green cultivation, and have broad application prospects in arid and semi-arid areas.
The research results were published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules under the title of Hydrogel synthesis based on lignin/sodium alginate and application in agriculture.
4. Developed lignin-based slow-release nitrogen fertilizer
Using industrial alkali lignin as raw material, a lignin-based slow-release nitrogen fertilizer with a nitrogen content of 10.13% was developed. Experiments show that most of the nutrients in the lignin-based slow-release nitrogen fertilizer will be gradually released after 28 days, and the slow-release effect is significant. It has opened up a new way for the development of new slow-release fertilizers, which can reduce nutrient loss and top dressing times, and improve fertilizer utilization efficiency. Of great significance.
The result was published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules under the title of Amination of biorefinery technical lignin by Mannich reaction for preparing highly efficient nitrogenfertilizer.

Preparation of nitrogen-doped porous carbon material-schematic diagram of adsorption mechanism
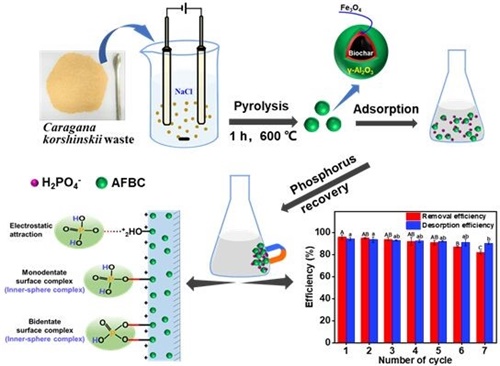
Development of biochar-based magnetic adsorbent and phosphate adsorption mechanism

Nano-cellulose/eucommia gum nano-composite film

CK: Control treatment without adding water retention agent; M: Self-made new water retention agent treatment; S: Tobacco growth status after different water treatments with acrylamide water-retaining agent

Preparation mechanism diagram of lignin-based slow-release nitrogen fertilizer
Editor in charge: Ye Ruiyou
Disclaimer: This article is translated by cpolymer. The translation is for reference only. All contents are subject to the original text.
Source: http://www.cas.cn/syky/202006/t20200603_4748786.shtml